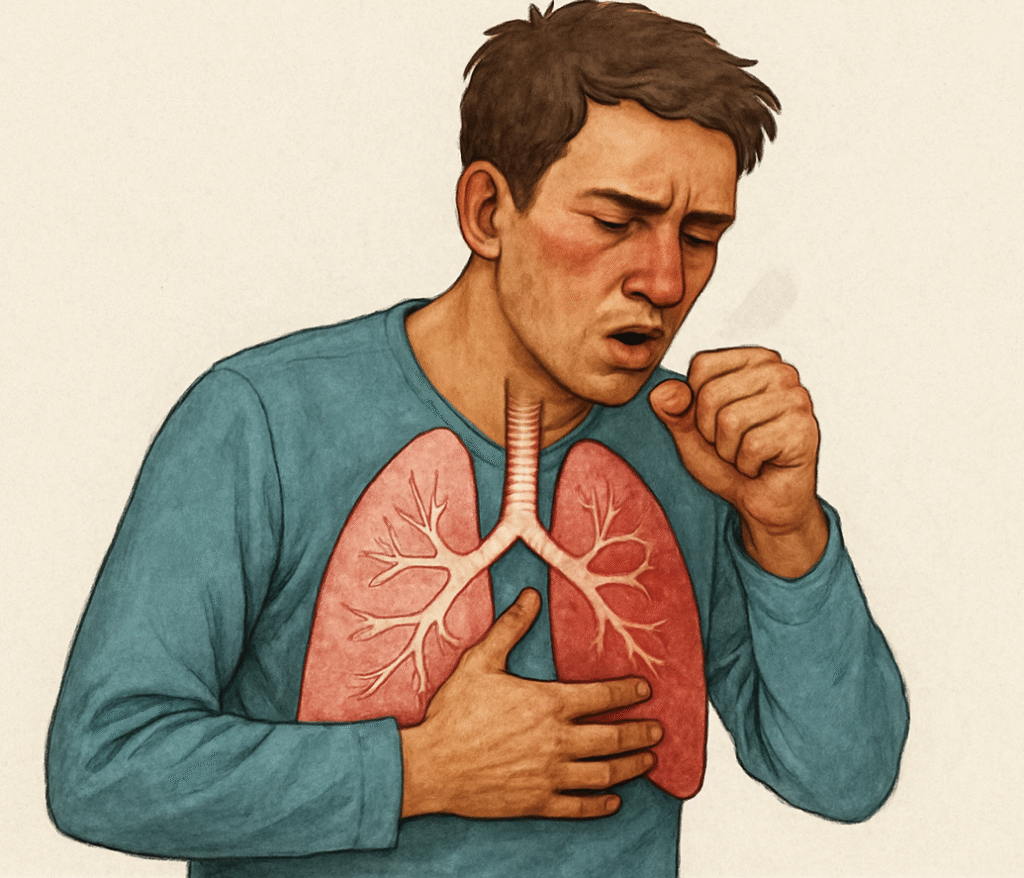
Pneumonia is a serious infection of the lungs that causes the air sacs (alveoli) to fill with fluid or pus. This makes breathing difficult and reduces oxygen supply to the body. Pneumonia can affect anyone but is most dangerous for infants, older adults, and people with weak immune systems.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The signs of pneumonia can vary from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Cough (with or without phlegm)
- Fever, chills, and sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (sometimes in children)
If symptoms worsen quickly or breathing becomes difficult, seek emergency care immediately.
Causes and Risk Factor
Pneumonia can be caused by:
- Bacteria: The most common cause, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viruses: Including influenza and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19).
- Fungi: More common in people with weakened immune systems.
You are at higher risk to get pneumonia if you:
- Are very young or elderly
- Smoke or have chronic lung disease
- Have a weakened immune system
- Have underlying conditions like diabetes or heart disease
- Are hospitalized or on a ventilator
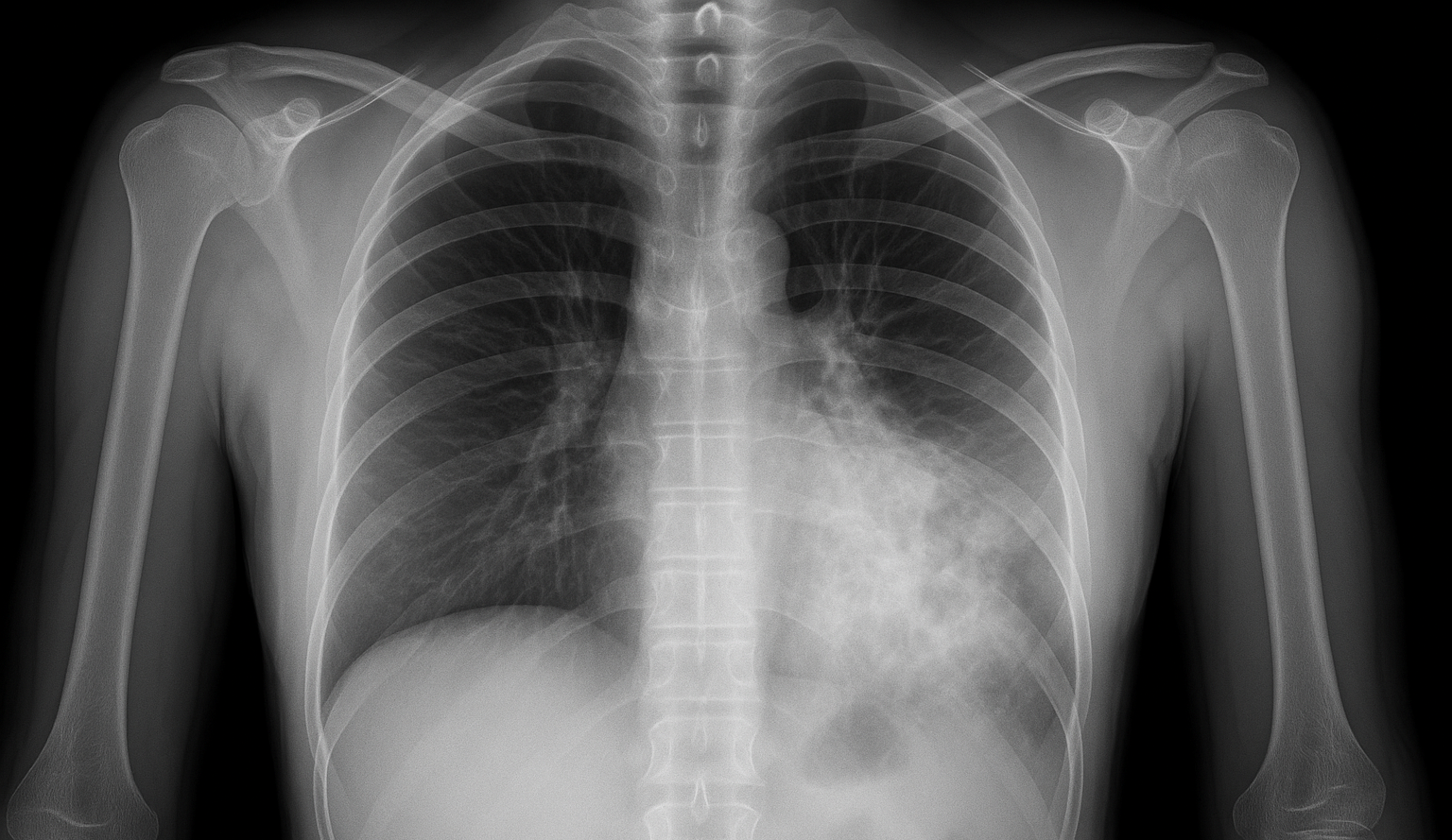
How to Diagnose Pneumonia?
Several examination and test were performed by doctors to confirm pneumonia:
- Physical exam (listening to the lungs).
- Chest X-ray to confirm infection.
- Blood tests to identify the cause.
- Sputum tests to check for bacteria.
What are the Treatment for Pneumonia?
Treatment depends on the cause:
- Bacterial pneumonia: Antibiotics.
- Viral pneumonia: Supportive care, rest, fluids, sometimes antivirals.
- Fungal pneumonia: Antifungal medication.
Supportive care includes:
- Rest and hydration
- Oxygen therapy for severe cases
- Hospitalization if breathing problems are serious
When to See a Doctor
See a doctor if you have:
- High fever with persistent cough
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Symptoms that worsen after a cold or flu
- Confusion or low energy (especially in elderly)
How to Prevent Pneumonia
You can lower risk of Pneumonia by:
- Getting vaccinated (pneumococcal vaccine, flu vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine).
- Practicing good hygiene (handwashing, mask use during outbreaks).
- Quitting smoking.
- Keeping the immune system strong with a healthy lifestyle.
Pneumonia remains a major global health concern and can cause serious health issues if not properly treated. By knowing the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods, you can protect yourself and seek care early if needed.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any health concerns.
Source:
You may also be interested in depression

[…] You may also be interested in pneumonia […]